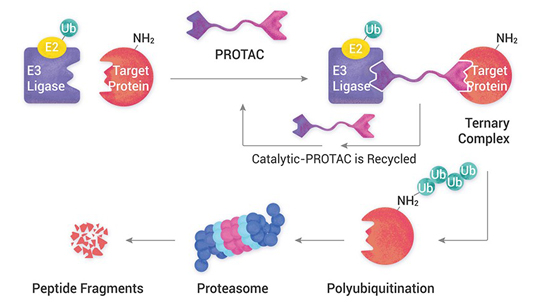
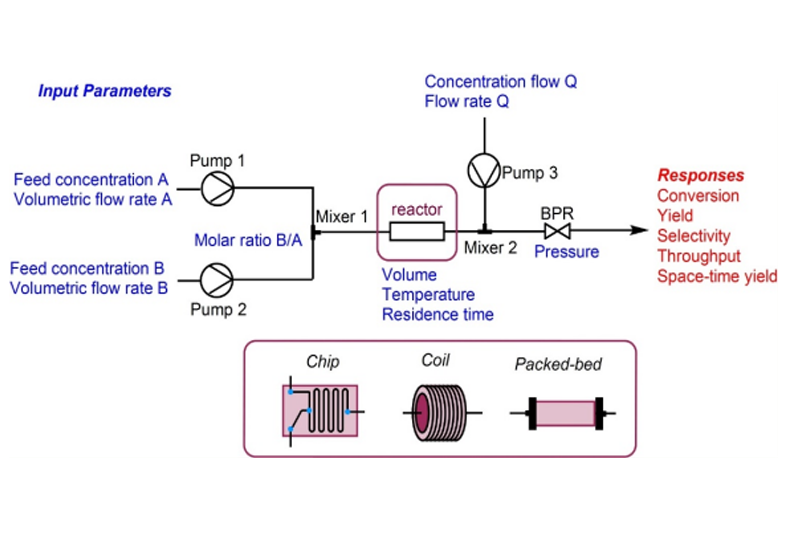
Aurigene offers GLP & Non-GLP bioanalysis services for small molecules, peptides, biomarkers and complex molecules. Our Bioanalytical labs are well-equipped with high-end LC-MS/MS instruments, HPLCs/UPLCs with UV, PDA and fluorescence detectors. We have completed more than 200 GLP studies. We perform sample analysis of GLP PK/TK/ TD studies. We do method validation as per regulatory requirement and ensure data quality and compliance.






Why Aurigene Pharmaceutical Services?
Delivered 200+ GLP studies
Compound management and data automation
Quality and Accuracy
Regulatory submissions to US FDA, EMA, DGCI
Connect with our scientific experts for your drug discovery, development, and manufacturing needs
We understand that clear communication is essential to successful collaborations, and that's why we have a dedicated team that is always ready to help you. Whether you have questions about our services, want to discuss a potential partnership, or simply want to learn more about our company, we're here to help.
Our team of experts is dedicated to providing personalised solutions tailored to your unique needs. So, please don't hesitate to reach out to us. We look forward to hearing from you and helping you achieve your business goals.
Resources
FEBRUARY 25, 2025
Transforming Drug Discovery with Aurigene.AI
In the early 2000s, developing Sovaldi, a hepatitis C treatment, took over a decade and nearly $2 billion. Similarly, Zolgensma, a gene therapy for spinal muscular atrophy, required 15 years due to its complexity. However, the advent of artificial intelligence (AI) has revolutionized drug discovery. For example, in 2022, Pfizer's PAXLOVID, an oral COVID...
Read More
Advancement in personalized medicine and how the CRDMO industry is part of the solution
Personalized medicine is transforming the healthcare landscape by customizing treatment plans to individual patients’ unique genetic, clinical and environmental characteristics. These are effective and less invasive treatments for a wide range of conditions. Contract Research, Development and Manufacturing Organizations (CRDMOs) play an important role...
Read More
Cell Line Development
We enable development of stable and high yielding recombinant Mammalian and Microbial lines. ...
Read MoreFamiliarization, process optimization, and cGMP manufacturing and supply of 30.0 kg of a Bioactive Nucleotide (NAD Booster)
Background: A US-based biopharmaceutical company approached Aurigene Pharmaceutical Services for the familiarization, process development, and cGMP manufacturing and supply of 30.0 kg Nucleotide product (NAD booster) for phase-appropriate studies. The synthesis of the desired product involves three linear stages, which starts with reaction of a pentose...
Read MoreIdentification of Degradants of Thermal and Oxidation Stress Studies of Empagliflozin and Linagliptin Tablets by HPLC-PDA and LC-MS Instrumental Techniques
2022
Objective of the manuscript is to identify the degradants observed in the thermal and oxidation degradation sample of Empagliflozin and Linagliptin tablets by using LC-MS and HPLC-PDA instrumental techniques. Thermal and oxidation degradation samples were injected in HPLC-PDA and LC-MS instruments. Mass of the degradants were detected by LC-MS technique, ...
Read More-
Discovery of MAP855, an Efficacious and Selective MEK1/2 Inhibitor with an ATP-Competitive Mode of Action.
2005
Mutations in MEK1/2 have been described as a resistance mechanism to BRAF/MEK inhibitor treatment. We report the discovery of a novel ATP-competitive MEK1/2 inhibitor with efficacy in wildtype (WT) and mutant MEK12 models. Starting from a HTS hit, we obtained selective, cellularly active ...
Read More -
Wang-OSO3H catalyzed green synthesis of bioactive isoindolo[2,1- a ]quinazoline-5,11–dione derivatives: An unexpected observation
2005
The sulphonic acid-functionalized Wang resin (Wang-OSO3H) was explored as a polymeric and recov- erable acidic catalyst for the synthesis of isoindolo[2,1- a ]quinazoline-5,11–dione derivatives under green conditions. Thus the Wang-OSO3H ...
Read More -
Polycyclic Aromatic Compounds: A Simple and Efficient [(n-Bu3Sn)2MO4]n Catalyzed Synthesis of Quinazolinones and Dihydroquinazolinones
2005
A novel unprecedented approach for the synthesis of various quinazolinones and dihydroquinazolinones has been using [(n-Bu3Sn)2MO4]n as a catalyst. The reaction has been screened ...
Read More
Frequently asked questions
What is pharmaceutical development?
Pharmaceutical development identifies and evaluates processes required to convert an NCE/drug substance into a drug product to deliver for its intended performance/purpose consistently. The pharmaceutical development process begins by measuring drug substance properties, identifying critical attributes of the drug product, checking absorption and stability profile of the drug, and the most appropriate route of administration (e.g. oral, parenteral, or topical).
Why is pharmaceutical development important at early drug development stage?
Pharmaceutical development evaluation already at the early drug development stage is essential for selecting the right NCE and formulation to reduce the attrition rate in the late-stage development. These activities streamline efficacy/toxicology evaluations, allowing pharmacologically effective and developable molecules to reach the clinic and eventually patients.
What are the advantages of integrated early-stage drug development?
The integration and close collaboration of preclinical and clinical development teams accelerate the FIH product development process by utilizing already available pre-formulation and bioavailability information and experience gained during preclinical formulation development. It also helps identify obstacles and apply the right formulation strategies early in the drug development process to avoid costly late-stage failures, significantly saving time and costs.
What is bioavailability?
The rate and extent to which the active ingredient or active moiety is absorbed from a drug product and becomes available at the biological system site.
What factors affect bioavailability?
The movement of the drug in the biological system is influenced by many factors such as routes of administration, physicochemical drug properties, physiological factors (e.g. gastrointestinal pH, gastric emptying, small intestinal transit time, bile salt, absorption mechanism, food, metabolism), manufacturing technique, dosage form, and excipients. Understanding the interrelationship of these factors leads to biopharmaceutical and science-based drug product developments.
Why is the oral bioavailability of drugs less than 100%?
Incomplete oral absorption could be due to poor solubility, poor intestinal permeability, or presystemic metabolism. Incomplete oral bioavailability can often be surmounted through formulation efforts.
How do you increase oral bioavailability?
We can enhance the oral bioavailability through formulation efforts using solubilizers, pH adjustment, cosolvents, complexing agents, permeation enhancers, and enabling technologies (solid dispersion, particle size reduction and lipid-based drug delivery systems).
br>By identifying potential limiting steps for oral absorption of a compound (including dissolution, solubility, permeability, and limited metabolism process), understanding the physicochemical properties of a compound, recognizing physiological processes affecting drug absorption, along with awareness of a drug's BCS and DCS characteristics, pharmaceutical scientist can better predict formulation approaches that can maximize the drug’s bioavailability.
Why is formulation development required at the preclinical drug development stage?
Formulations play a crucial role in assessing the biological properties of a molecule during drug discovery. Maximizing exposure is the primary objective of early animal experimentation to avoid discarding developable compounds with the desired pharmacologic properties.
Diversity in the physiology between various animal species, routes of administration, limited compound amount, and limitations posed by specific pharmacological models make formulation development much more challenging. Consistency in the exposure is also a key aspect as significant variations are observed in early NCE batches.
Additionally, preclinical tox (GLP) studies at early development, require NCE formulations that are simple, robust, provide ease of preparation, convenient to deliver to animals with minimal ancillary effects of vehicle and provide provision of high and dose-related systemic exposures in animals relative to anticipated human exposures to facilitate determination of tox profiles.
The selection and development of effective formulation and drug delivery strategies are essential to achieve this.
You are about to leave Aurigene Pharmaceutical Services and affiliates website. Aurigene Pharmaceutical Services assumes no responsibility for the information presented on the external website or any further links from such sites. These links are presented to you only as a convenience, and the inclusion of any link does not imply endorsement by Aurigene Pharmaceutical Services.
If you wish to continue to this external website, click Proceed.


Leaving already?
Don't forget to join us at
CPHI Worldwide 2023.
October 24th-26th, 2023 | Barcelona, Spain
Get ready to accelerate your drug’s journey to the market