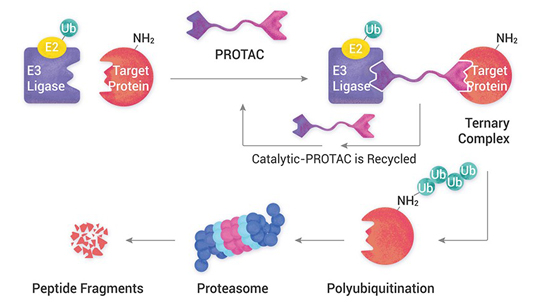
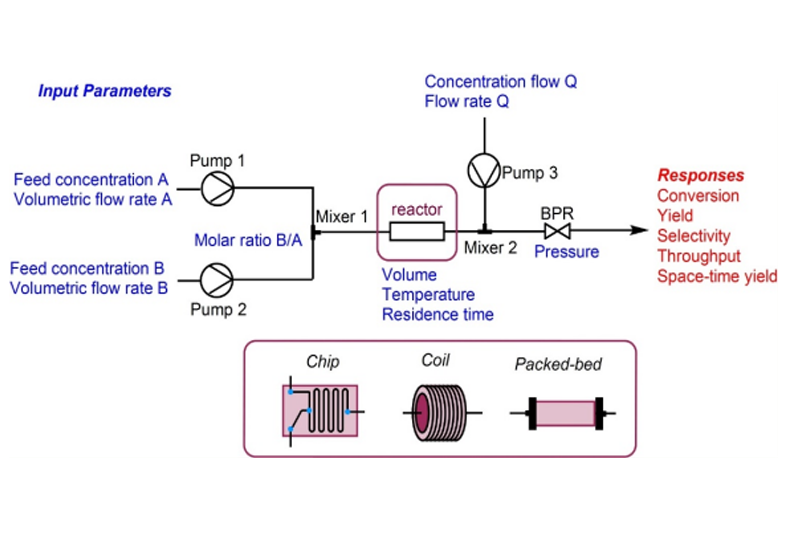
Preclinical genetic toxicology studies are crucial for assessing the potential genetic risks of new drugs and chemicals before they are tested in humans. These studies help identify substances that may cause genetic mutations, chromosomal damage, or other genetic alterations that could lead to cancer or other genetic diseases. Here's a comprehensive overview of our capabilities at Aurigene:
- Mutagenicity Testing: To determine if a substance can cause genetic mutations.
- Clastogenicity Testing: To assess if a substance can cause structural changes in chromosomes.
- Genotoxicity Testing: To evaluate the overall potential of a substance to damage genetic material.


Why Aurigene Pharmaceutical Services?
Quick turnaround time
Extensive experience in the genetic toxicology studies
Team of expert analytical and toxicology scientists
State-of-the-art facilities
Connect with our scientific experts for your drug discovery, development, and manufacturing needs
We understand that clear communication is essential to successful collaborations, and that's why we have a dedicated team that is always ready to help you. Whether you have questions about our services, want to discuss a potential partnership, or simply want to learn more about our company, we're here to help.
Our team of experts is dedicated to providing personalised solutions tailored to your unique needs. So, please don't hesitate to reach out to us. We look forward to hearing from you and helping you achieve your business goals.
Resources
FEBRUARY 25, 2025
Transforming Drug Discovery with Aurigene.AI
In the early 2000s, developing Sovaldi, a hepatitis C treatment, took over a decade and nearly $2 billion. Similarly, Zolgensma, a gene therapy for spinal muscular atrophy, required 15 years due to its complexity. However, the advent of artificial intelligence (AI) has revolutionized drug discovery. For example, in 2022, Pfizer's PAXLOVID, an oral COVID...
Read More
Advancement in personalized medicine and how the CRDMO industry is part of the solution
Personalized medicine is transforming the healthcare landscape by customizing treatment plans to individual patients’ unique genetic, clinical and environmental characteristics. These are effective and less invasive treatments for a wide range of conditions. Contract Research, Development and Manufacturing Organizations (CRDMOs) play an important role...
Read More
Cell Line Development
We enable development of stable and high yielding recombinant Mammalian and Microbial lines. ...
Read MoreFamiliarization, process optimization, and cGMP manufacturing and supply of 30.0 kg of a Bioactive Nucleotide (NAD Booster)
Background: A US-based biopharmaceutical company approached Aurigene Pharmaceutical Services for the familiarization, process development, and cGMP manufacturing and supply of 30.0 kg Nucleotide product (NAD booster) for phase-appropriate studies. The synthesis of the desired product involves three linear stages, which starts with reaction of a pentose...
Read MoreIdentification of Degradants of Thermal and Oxidation Stress Studies of Empagliflozin and Linagliptin Tablets by HPLC-PDA and LC-MS Instrumental Techniques
2022
Objective of the manuscript is to identify the degradants observed in the thermal and oxidation degradation sample of Empagliflozin and Linagliptin tablets by using LC-MS and HPLC-PDA instrumental techniques. Thermal and oxidation degradation samples were injected in HPLC-PDA and LC-MS instruments. Mass of the degradants were detected by LC-MS technique, ...
Read More-
Discovery of MAP855, an Efficacious and Selective MEK1/2 Inhibitor with an ATP-Competitive Mode of Action.
2005
Mutations in MEK1/2 have been described as a resistance mechanism to BRAF/MEK inhibitor treatment. We report the discovery of a novel ATP-competitive MEK1/2 inhibitor with efficacy in wildtype (WT) and mutant MEK12 models. Starting from a HTS hit, we obtained selective, cellularly active ...
Read More -
Wang-OSO3H catalyzed green synthesis of bioactive isoindolo[2,1- a ]quinazoline-5,11–dione derivatives: An unexpected observation
2005
The sulphonic acid-functionalized Wang resin (Wang-OSO3H) was explored as a polymeric and recov- erable acidic catalyst for the synthesis of isoindolo[2,1- a ]quinazoline-5,11–dione derivatives under green conditions. Thus the Wang-OSO3H ...
Read More -
Polycyclic Aromatic Compounds: A Simple and Efficient [(n-Bu3Sn)2MO4]n Catalyzed Synthesis of Quinazolinones and Dihydroquinazolinones
2005
A novel unprecedented approach for the synthesis of various quinazolinones and dihydroquinazolinones has been using [(n-Bu3Sn)2MO4]n as a catalyst. The reaction has been screened ...
Read More
You are about to leave Aurigene Pharmaceutical Services and affiliates website. Aurigene Pharmaceutical Services assumes no responsibility for the information presented on the external website or any further links from such sites. These links are presented to you only as a convenience, and the inclusion of any link does not imply endorsement by Aurigene Pharmaceutical Services.
If you wish to continue to this external website, click Proceed.


Leaving already?
Don't forget to join us at
CPHI Worldwide 2023.
October 24th-26th, 2023 | Barcelona, Spain
Get ready to accelerate your drug’s journey to the market